- Transaction description : Central User Administration Log
- Module : BC-SEC-USR-ADM (User and Authorization Management)
- Parent Module : BC (Basis Components)
- Package : SUSR (ABAP User Administration)
- ABAP Program : SAPMUSLG
SCUL related transactions | |
|---|---|
| Tcode | Note |
| RSUSR_SYS_LIC | Cross-System License Data Info. |
| SALE_CUA | Display ALE Customizing for CUA |
| SCUA | Central User Administration |
| SCUC | CUA: Synchronize company addresses |
| SCUG | Transfer Users |
| SCUH | Change Documents for CUA Landscape |
| SCUL | Central User Administration Log |
| SCUM | Central User Administration |
| SU0 | Maintain Own Fixed User Values |
| SU01 | User Maintenance |
| SU01D | User Display |
| SU01_NAV | User maint. to include in navigation |
| SU01_OLD | User Maintenance |
| SU02 | Maintain Authorization Profiles |
| SU03 | Maintain Authorizations |
| SU1 | Maintain Own User Address |
| SU10 | User Mass Maintenance |
| SU10_OLD | User Mass Maintenance |
| SU12 | Mass Changes to User Master Records |
| SU2 | Maintain Own User Parameters |
| SU20 | Maintain Authorization Fields |
| SU20_BTCH | Maintain Authorization Fields |
| SU21 | Maintain Authorization Objects |
| SU21_OLD | Maintain Authorization Objects |
| SU22 | Maintain Authorization Defaults(SAP) |
| SU3 | Maintain Users Own Data |
| SU3_OLD | Maintain Users Own Data |
| SU50 | Own data |
| SU51 | Maintain Own User Address |
| SU52 | Maintain Own User Parameters |
| SU53 | Evaluate Authorization Check |
| SU56 | Analyze User Buffer |
| SU80 | Archive user change documents |
| SU81 | Archive user password change doc. |
| SU82 | Archive profile documents |
| SU83 | Archive authorization docs. |
| SU84 | Read Archived User Change Documents |
| SU85 | Read Archived Password Change Doc. |
| SU86 | Read Profile Change Documents |
| SU87 | Read Authorization Change Documents |
| SU96 | Table maint.: Change SUKRIA |
| SU97 | Table maint.: Display SUKRIA |
| SU98 | Call Report RSUSR008 |
| SU99 | Call report RSUSR008 |
| SUCOMP | User company address maintenance |
| SUGR | Maintain User Groups |
| SUGRD | Display user groups |
| SUGRD_NAV | Display User Groups |
| SUGR_NAV | Maintain User Groups |
| SUUM | Global User Manager |
| SUUMD | Display User Administration |
| SU_REFUSERVARIABLE | Maintain reference user variables |
| SU_VCUSRVARCOM_CHAN | Maintain View Cluster VCUSRVARCOM |
| SU_VCUSRVARCOM_DISP | Display View Cluster VCUSRVARCOM |
| SU_VCUSRVAR_CHANGE | Maintain View Cluster VCUSRVAR |
| SU_VCUSRVAR_DISP | Display View Cluster VCUSRVAR |
| S_BCE_68001393 | Users by address data |
| S_BCE_68001394 | Users According to Complex Criteria |
| S_BCE_68001395 | Users According to Complex Criteria |
| S_BCE_68001396 | Users According to Complex Criteria |
| S_BCE_68001397 | Users According to Complex Criteria |
| S_BCE_68001398 | Users According to Complex Criteria |
| S_BCE_68001399 | Users According to Complex Criteria |
| S_BCE_68001400 | Users According to Complex Criteria |
| S_BCE_68001401 | Critical Combinations of Auth. |
| S_BCE_68001402 | With Unsuccessful Logons |
| S_BCE_68001403 | With Critical Authorizations |
| S_BCE_68001404 | Profiles by Contained Profiles |
| S_BCE_68001405 | Profiles by Authorization Name |
| S_BCE_68001406 | Profiles by Values |
| S_BCE_68001407 | Profiles by Changes |
| S_BCE_68001408 | Profiles by Roles |
| S_BCE_68001409 | Profiles According to Complex Crit. |
| S_BCE_68001410 | Auth. Objects According to Complex |
| S_BCE_68001411 | Auth. Objects According to Complex |
| S_BCE_68001412 | Auth. Objects According to Complex |
| S_BCE_68001413 | Auth. Objects According to Complex |
| S_BCE_68001414 | Auth. According to Complex Criteria |
| S_BCE_68001415 | Authorizations by Values |
| S_BCE_68001416 | Authorizations by Changes |
| S_BCE_68001417 | Auth. According to Complex Criteria |
| S_BCE_68001418 | Roles by Role Name |
| S_BCE_68001419 | Roles by User Assignment |
| S_BCE_68001420 | Roles by Transaction Assignment |
| S_BCE_68001421 | Roles by Profile Assignment |
| S_BCE_68001422 | Roles by Authorization Object |
| S_BCE_68001423 | Roles by Authorization Values |
| S_BCE_68001424 | Roles by Change Data |
| S_BCE_68001425 | Roles by Complex Criteria |
| S_BCE_68001426 | Transactions for User |
| S_BCE_68001427 | Transactions for User |
| S_BCE_68001428 | Transactions for User |
| S_BCE_68001429 | Transactions for User |
| S_BCE_68001430 | Compare Users |
| S_BCE_68001431 | Compare Profiles |
| S_BCE_68001432 | Compare Authorizations |
| S_BCE_68001433 | Comparisons |
| S_BCE_68001434 | Where-used lists |
| S_BCE_68001435 | Where-used lists |
| S_BCE_68001436 | Where-used lists |
| S_BCE_68001437 | Where-used lists |
| S_BCE_68001438 | Where-used lists |
| S_BCE_68001439 | For user |
| S_BCE_68001440 | For profiles |
| S_BCE_68001441 | For authorizations |
| S_BCE_68001767 | By Profile Name or Text |
| S_BCE_68001777 | Compare Roles |
| S_BCE_68001821 | . |
| S_BCE_68001822 | . |
| S_BCE_68002030 | Where-Used List for Authorization |
| S_BCE_68002041 | Executable for Role |
| S_BCE_68002111 | Users with Critical Authorizations |
| S_BCE_68002311 | Change Documents for Users |
| S_BIE_59000197 | Report cross-system information |
| S_BIE_59000198 | Report cross-system information |
| S_BIE_59000199 | Report cross-system information |
| S_YI3_39000067 | Where-Used List for Sec. Policies |
- SCUM SAP tcode - Central User Administration SCUM (Central User Administration) is a standard SAP transaction code available within R/3 SAP systems depending on your version and release level. Below for your convenience is a few details about this tcode including any standard documentation available.
- SCUM SAP tcode - Central User Administration SCUM (Central User Administration) is a standard SAP transaction code available within R/3 SAP systems depending on your version and release level. Below for your convenience is a few details about this tcode including any standard documentation available.
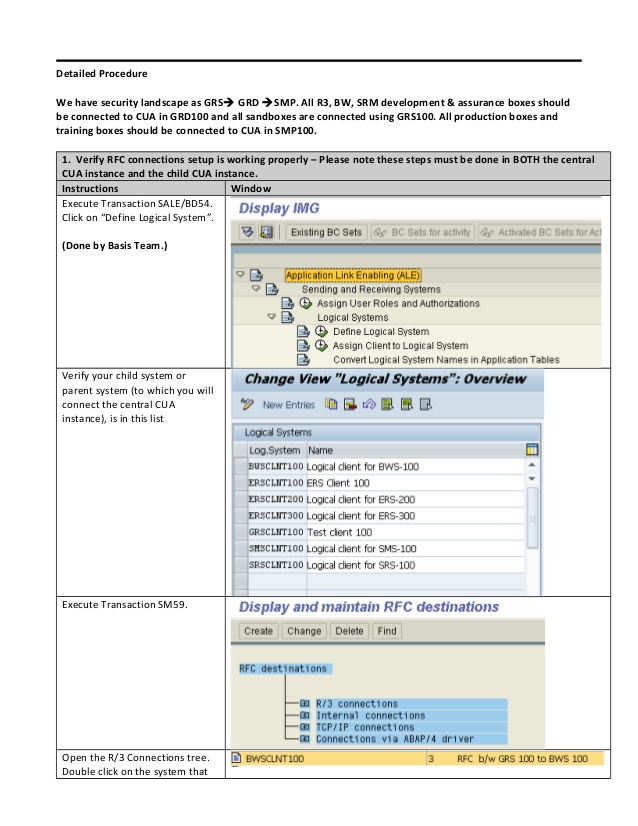
As we have seen the overview of CUA in our pervious blog, now, I will explain the procedure to set up the CUA. At macro level details, below steps need to be performed to set up the CUA:
OAA1 SAP ArchiveLink: Maint.user st.syst OAA3 SAP ArchiveLink protocols OAA4 SAP ArchiveLink applic.maintenance OAAD ArchiveLink Administration Documents OAC2 SAP ArchiveLink: Globaldoc. Types OAC5 SAP ArchiveLink: Bar code entry OACA SAP ArchiveLink workflow parameters OAD0 SAP ArchiveLink: Objectlinks OAD2 SAP ArchiveLink document classes. When executing t-code SCUG to import the users from the child system, some users, that exists in just one. But, if one user exists in more than one client and it appears in 'Identical users' tab of SCUG, after importing this user, when editing. In SU01, a dump occurs. How to maintain the user Company address in SAP Author Techrelam. Posted-on 21:48. Maintain Company address for User in SAP.
Steps to Set Up the CUA
- Create Administrator
- Specify Logical systems
- Assign logical systems to client
- Create system users
- Create RFC destinations
- Create CUA
- Set field distributor parameters
- Synchronization of company addresses
- Transfer Users
Below are the systems considered as an example to set up CUA:
- System ABC with client 123
- System PQR with client 456
- System XYZ with client 789
Here, we will set system ABC (client 123) as a CUA central system and other systems as child systems. As per this structure, we will proceed with above mentioned steps:
1. Create Administrator User
SALE_CUA
In a completely new system that is to be set up, an administration user needs to be created with which all further steps can be performed. To create such administrator user:
- Login to all systems with user SAP* and create the user in t-code SU01
- Assign the relevant administrator role to user
- Apply the security measures to secure SAP* user against misuse
2. Specify Logical systems
In CUA landscape, SAP systems are identified with Logical system names. Due to this, Logical systems need to be created for every system which is going to be included in CUA landscape. This is one time task to be performed before setting up CUA. The Logical systems can be defined be following below steps:
- Login to system ABC (client 123) with administrator user created in step 1
- Go to t-code BD54 You can; alternatively maintain the table view V_TBDLS using transaction SM30.
- Choose Edit ? New Entries
- In the LogSystem column, create a new logical name in capital letters for every CUA system (that is, for the central and all child systems including those from other SAP Systems). Here, the standard naming convention for logical system is <System ID>CLNT<Client>. In this way, the below logical systems will be created in CUA central system (ABC system):
- ABCCLNT123
- PQRCLNT456
- XYZCLNT789
In the same way, create the logical system name for the central system in all child systems.
3. Assign logical systems to client
We need to perform this cross-client procedure only once for each SAP system as per below procedure:
- Login with administrator user and execute the t-code SCC4
- Switch to change mode
- Call the detail display of the client that you want to assign a logical system by double clicking on the line of the client
- In the Logical System field, specify the name of the logical system to which the selected client is to be assigned
Ex: – If we execute the t-code SCC4 in system ABC then, open the client 123 and maintain the logical system name as ABCCLNT123
4.Create system users
System users are required for the internal communication of the systems in an ALE group. These system users, defined in the target systems, are entered in RFC destinations in the calling systems.
Note: – No license fees apply to these system users.
To simplify the maintenance of system users, use the following naming conventions:
- In the central system (system ABC), the naming convention will be CUA_<system Id>. This system user is used in the RFC destinations from child to central system. With this naming convention, we need to create the system user in system ABC with name: CUA_ABC
- In the child systems, the naming convention CUA__<System Id>_<Client>. These system users are used in the RFC destinations from central to child system. With this naming convention, we need to create the system users as below:
Sap Tcode Table
Below are SAP delivered roles for system users which need to be copied to customer namespace before assigning them to system users.
Scug Tcode In Sap Data Management
Roles in Central system:
- SAP_BC_USR_CUA_SETUP_CENTRAL
- SAP_BC_USR_CUA_CENTRAL
- SAP_BC_USR_CUA_CENTRAL_BDIST
Roles in child system:
- SAP_BC_USR_CUA_SETUP_CLIENT
- SAP_BC_USR_CUA_CLIENT
With these details, we need to create the respective users with their applicable authorizations in t-code SU01 as below:
5. Create RFC destinations
Till this step, we are ready with Logical systems and system users, Now, we need to create RFC connections between the systems as mentioned in below steps:
- Login to central system ABC, execute the t-code SM59 and Choose Create.
- Enter the following data:
Note: – You must create the name of the RFC destination in capital letters.
- Confirm your entries with ENTER
- Choose the option Host Name for Save as and Confirm your entries with ENTER
- Specify the name of the SAP system of the child system (such as PQR) in the target system ID field. To do this, overwrite the automatic entry.
- Specify the message server of the target system in the MessageServer field. To do this, overwrite the automatic entry.
- Save your entries.
- To define the return connection, repeat the procedure in the child system for the central system
- To determine whether the network connection between the two systems is functioning correctly, choose Test Connection.
In this way, we have created the RFC connections (with names identical to Logical system name of target system) in each SAP systems.
6. Create CUA
Till now, we have connected all the systems ABC, PQR and XYZ as in below figure:
Now, we will define the system ABC as CUA in this landscape as detailed in below steps:
- Login to system ABC and execute the t-code SCUA
- Enter the name of your distribution model, such as CUA.
- Choose Create.
- Enter the name of the child systems viz. PQRCLNT456 and XYZCLNT789
- Save your entries.
In this way, we have defined the system ABC as central system. After completion of this step, you can no longer create user master records in the child systems.
7. Set field distributor parameters
In Central User Administration, we can use the distribution parameters in transaction SCUM to determine where individual parts of a user master record are maintained.
- In the central system
- Locally in the child system
- In the child system with automatic redistribution to the central system and the other CUA child system
Every input field of the user maintenance transaction SU01 has a field attribute that you set once in the central system with transaction SCUM during Customizing. To perform this customizing, perform the below steps:
- Login to system ABC and execute the t-code SCUM
The system displays the User Distribution Field Selection screen, with tab pages of the fields whose distribution parameters you can set. You can select the following options on the tab pages:
- To maintain the other parameters, too, switch to the other tab pages. The tab pages correspond to those of user maintenance.
- Save your entries. The distribution parameters are automatically transferred to the child systems.
8. Synchronization of company addresses
The company addresses are maintained in individual systems PQR and XYZ. To enable CUA to communicate properly you must ensure that at least the central system contains complete information about all valid company addresses. You then distribute this complete company address set to all child systems, meaning that there is a consistent status of company addresses in the entire CUA.
Steps:
- Login to central system ABC and execute the t-code SCUG
- Select the first child system PQR and choose Synchronize Company Addresses in the Central System
- Process all sub lists for the address categories in succession and repeat the above steps for system XYZ
- Choose Back to start the address distribution from the central system.
- Choose Distribute Synchronized Company Addresses to target Systems icon.
9. Transfer Users
As soon as we have configured the CUA, the users from child systems need to be transferred to Central system so that we can see their authorization details (such as roles to be assigned to users for child system and the roles assigned to them). The procedure is given in below steps:
- Login to central system ABC and execute the t-code SCUG
- Place the cursor on central system name appeared on the screen and click on the Transfer Users.
- The system displays the following tab pages:
- Select all new and changed users and choose Transfer Users.
- Perform the above 2 steps for child systems PQR and XYZ
- After you have completed the user transfer, remove the roles Z_SAP_BC_CUA_SETUP_CENTRAL and Z_SAP_BC_USR_CUA_SETUP_CLIENT from the system users.
At this stage, the CUA set up is completed.
